Explainers
A phone’s water protection plan: IP ratings explained
It doesn’t give you the right to dunk it in water, though
If you plan to bring your phone to a beach trip with your friends, you normally bring a pouch with you. The main function of that pouch is to protect your phone from contact with any liquid while you enjoy the waves. Of course, it doesn’t fully guarantee that water won’t seep through it — especially when a big wave crashes on you and opens the pouch. But, it does give a sense of safety and security for your beloved smartphone.
That’s the whole concept behind an IP rating that’s given to most smartphones today. Nowadays, you hear a lot about these smartphones being advertised with IP68 ratings. But, what does an IP68 rating actually mean? Is it worth something to consider when buying a new smartphone?
What is an IP rating?
IP ratings are not new in the tech world. In fact, a lot of the electrical appliances and technologies you have at home come with it. An IP rating, or ingress protection rating basically tells you the level of protection any electrical device has against solid and liquid objects. It acts as a security measure to determine what objects the device can handle without malfunctioning.
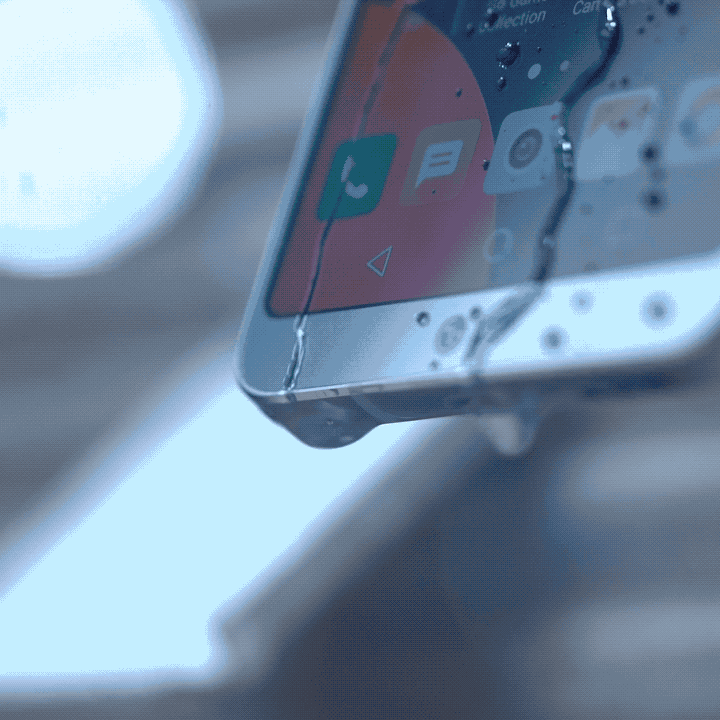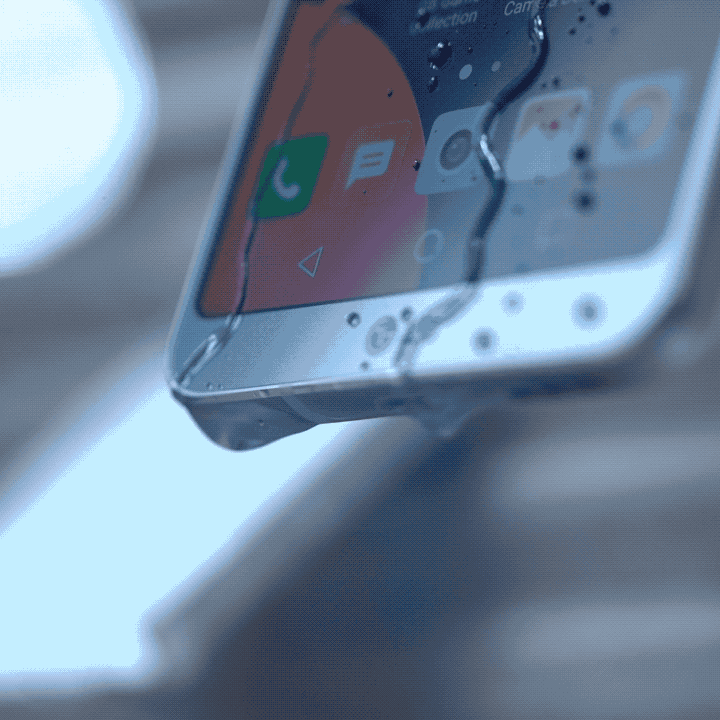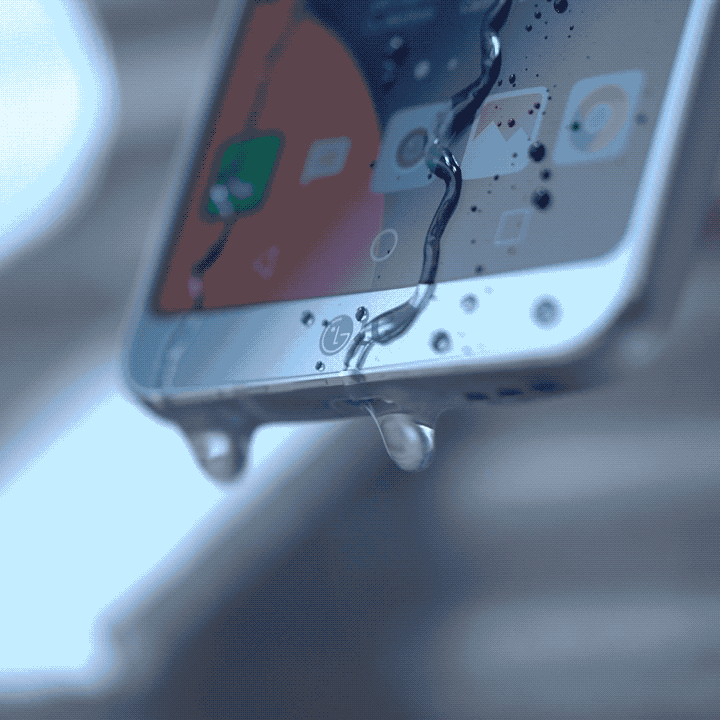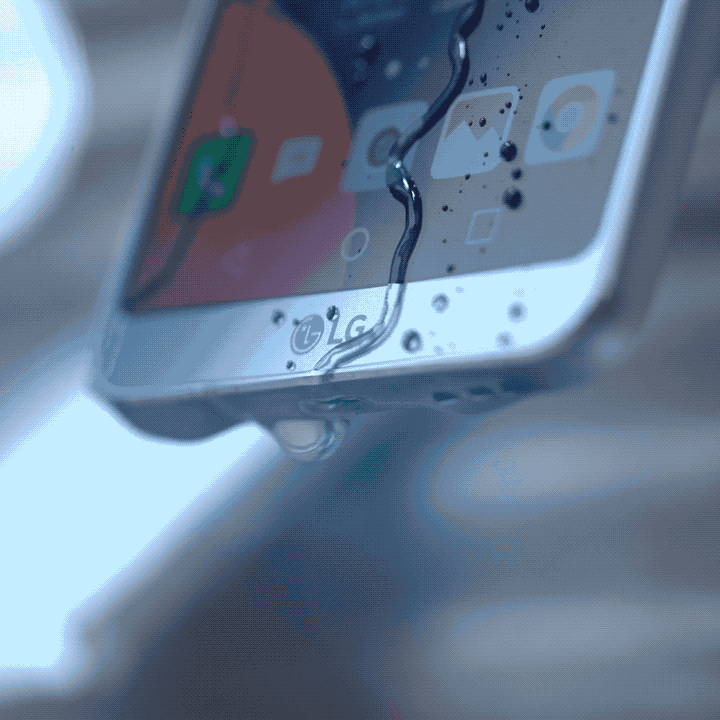
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) gives out these ratings to manufacturers as a safety measure for production. It consists of two numbers that describe its protection against a vast number of objects, even human touch. The first number denotes a device’s protection against common solid objects and dust. Meanwhile, the second number denotes a device’s protection against liquids, even steam-jet liquids. The higher the number, the more protection it gets!
IP ratings are not just present in most recent smartphones. Things like electrical sockets, cameras, even phone cases come with IP ratings, as well.
The reason it exists
Manufacturers and consumers see an IP rating quite differently. Those two numbers ultimately stand for how well your device can stand against, well anything. For manufacturers, an IP rating basically gives them a standard to follow when producing more devices. Before shipping their latest smartphones, they subject their devices to numerous tests to validate their IP ratings.
Also, it gives a more concrete way of stating that their devices are resistant to such objects. When you come across smartphones that claim to be water resistant, oftentimes you tend to ask just how resistant it is. With manufacturers, the IP rating gives a more definitive measure to that claim. For example, a smartphone with an IP68 rating is heavily protected against dust, and you can submerge it in waters deeper than a meter — perfect for beach trips.
For consumers, the IP rating just provides a peace of mind when buying a new smartphone. It’s basically placed there to tell you that your phone can still be used even if you subject it to too much dust or water that’s too deep. You see this in most YouTube videos or channels that basically bend, scratch, and dunk phones in buckets of water. In the end, you won’t have to worry about destroying your phone that much when you go on that beach trip without a pouch.
Some manufacturers simply don’t need the rating
However, there are manufacturers that simply found the rating unnecessary or simply just a marketing tool. Companies like OnePlus even did an entire ad that showed off their new flagship devices, the OnePlus 7 and OnePlus 7 Pro without an IP rating. The whole issue sparked debates on whether or not IP ratings do make sense, or companies could simply do without them.
OnePlus argues that one reason their new smartphones don’t have an IP rating is because of the cost to get one. Even simply requesting for a phone for consideration costs a lot on the manufacturing side, which ultimately bumps up the phone’s price. Pete Lau, one of the co-founders of the company estimated the cost for getting an IP rating is at US$ 30. Of course, it is entirely up to the consumer’s view of its value to the overall product.
The other reason is because of the coverage of the device’s warranty, particularly towards water damage. OnePlus claims that even if smartphones have IP ratings that show how resistant they are to water, water damage isn’t fully covered by its warranty. This also furthers their argument on why they wouldn’t want to spend on getting one in the first place. An IP rating is not a legitimate reason for people to have their phones fixed for free after dunking them in buckets of water.
To them, it does not make sense to simply attach an IP rating onto a phone even as a marketing tool. It gives off the wrong impression that the device is waterproof when the rating basically leans towards phones being water resistant.
Do we really need to know the IP rating?
The IEC created IP ratings for everyone’s protection — from manufacturers to consumers. The whole purpose of having an IP rating is to provide a level of protection for anything electrical, smartphones included. It ensures the safety of everyone, but it’s not a way to bail anyone out when they dunk their phones in water.
While some may argue that it helps to know what your device’s IP rating is for better care, others just see it as a marketing ploy. It only seeks to sell a device perceived to be waterproof according to a standard. However, IP ratings were not meant to waterproof your phone by any means. It’s there to tell you that your phone can handle water, just possibly not too much.
At the end of the day, we have to ask ourselves whether we truly see the value in having these IP ratings. Whether or not your preferred device has an IP rating, just remember: it’s not a reason for you to exploit your phone.

Explainers
ChatGPT Explained: Should we be scared of AI?
Will the talking robot take over the world?

Back in the earlier days of the internet, an emerging but short-lived trend involved chatbots who could generate conversation with whomever it talked to. Does this sound familiar? Today, a similar phenomenon is creating a lot of waves online, headed by the infamous ChatGPT. The exceedingly popular ChatGPT is turning heads out of fear that the technology will eventually upend society and eradicate a lot of jobs.
But what exactly is ChatGPT? How is it different from language programs in the past? Is the world right to worry about them?
On the rise of language learning
ChatGPT is hardly the first software to inexplicably generate comprehensible dialogue without human intervention. Decades ago, the internet hosted rudimentary versions of today’s chatbot technology. The concept is somewhat similar, though. The early versions relied on a database of responses from human users. If you asked about coffee, for example, the answer you get will likely come from the logs of another user who talked about coffee in the past.
Because the system was imperfect in its infancy, part of the appeal was trying to get the software to fumble a conversation. However, if it did mess up, you can count on it asking you what it should have said. The next time someone asks the same question, the software might mirror what you said, creating a learning process between the software and the user.
Today, chatbots — meaning those usually used by businesses today — operate in the same way. If a customer comes with a query, the software will rely on a set of responses to most appropriately address the user’s problem. If the software can’t come up with a solution, the ball usually gets passed on to a human consultant.
Is ChatGPT just another chatbot?
Though the label certainly gets thrown around, ChatGPT isn’t strictly a chatbot. Instead, the software uses GPT-3.5, a specific language model created by OpenAI. Whereas early and more rudimentary versions of the same technology can already store an unbelievable amount of information in its memory, ChatGPT can analyze billions of words and the relationship between them.
Further, OpenAI extensively trains the software, ensuring that comprehension and grammar can live up to today’s standards. The learning is supervised. In fact, the company even has a makeshift reward system to ensure that the software puts out the most appropriate response. With users also contributing to the software’s learning process, ChatGPT is quickly emerging as a powerhouse for the technology.
The results speak for themselves. While users can generate simple conversations with the software, ChatGPT can just as easily answer more extensive queries with lengthier responses. If you ask it to create an essay about Christopher Columbus, for example, it can write a lengthy piece that can easily fool a casual reader. It can even handle more speculative queries. In a sample published by the developer, ChatGPT can answer what would happen if Columbus discovered America in 2015.
What’s it good for?
Based solely on what the software can do, ChatGPT can find its purpose in today’s world. The software can improve voice assistants and chatbots all over the internet. It can make big strides in the world of automation, enabling a more responsive interface between user and software.
On a more human aspect, the software can also handle more professional jobs with simpler prompts such as those involving simple marketing copy. It can help with more ephemeral research efforts, allowing users to get simple answers for otherwise complex questions.
And, on a more technical side, ChatGPT can reportedly analyze and detect what’s wrong with a piece of coding. With the software, developers can use ChatGPT to potentially repair code without having to pore over every single line. Allowing a powerful tool to inspect code speaks volumes for a lot of applications all over the world including smart vehicles and technical machinery.
However, as with every piece of technology, users will always find a way to use something beyond what it was originally designed for. ChatGPT is now changing the world of education as students are using the software to do their homework for them. Though a lot of the sample texts look like they can fool only lower levels of education, a Wharton business school professor (via Business Insider) recently stated that he would have been fooled by a ChatGPT essay, grading a sample with a passable grade of B or B-.
Should we be scared of ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is undoubtedly rocking the world of education. While some schools have banned the technology outright, others are debating on the software’s impact on how schools are taught. Since ChatGPT deals out more factual information, could education reinvent itself to teach more personal, tailored learning, rather than just the ability to spit out memorized facts. (“Factual” might even be an exaggeration. CNET, which recently experimented with AI-written articles, discovered a plethora of errors from using the software.)
Now, education isn’t the only world in peril. The creative industry is facing an extreme challenge wherein ChatGPT can potentially cause workers their jobs. Though the danger certainly seems real, the limitations of technology are also real. ChatGPT can create comprehensible text that can fool a human, but it will likely stumble with conceptualization.
A piece of software is just software. Even if it can write an essay about existentialism, it cannot think of the concept metaphysically. In the same way, even if it can show you a photo of a parrot, it cannot think of that photo as anything but a pattern of pixels. To a language learning software, words don’t mean anything else besides their relationship with each other. It’s the same thought process as a dog learning to run to its human when its name is called. The dog doesn’t know that you just said its name (or even the mere concept of a name); it just knows to do a certain action after hearing a specific sound.
Can ChatGPT change the world? Overall, the jury is still out, but it’s unlikely that a piece of learning software can do much to replace human-centric work. Regardless, it’s important to think of how ChatGPT can improve (or detriment) humanity.
Like with other supposedly dangerous technology, the world of technology is a Pandora’s box. We can never put the genie back into the bottle. Once it’s out, it’s out. Instead of worrying about how technology can destroy the world, the more appropriate response is to figure out how it can better humanity without sacrificing anyone’s wellbeing in the process.

When you’re looking to buy a new device, which specs should you pay attention to? Which upgrades should you consider?
In this video instead of reviewing the latest new smartphone, we’re going to talk about its unsung hero: RAM.
We partnered with @MicronTech to help you understand all the magical things that you get to do on your smartphone thanks to internal memory and storage.
To find out more about Micron’s mobile memory and storage solutions and how they’re bringing mobile innovation to life, visit https://www.micron.com/solutions/mobile or watch our explainer video.

If you watched the latest Far Out event from Apple, you might have noticed the debut of a new technology coming to smartphones: satellite connectivity. Though Apple has made the biggest deal of the new feature, the technology has existed even before Apple’s announcement. In fact, various smartphone makers are also announcing their own takes to go along with Apple’s satellites.
But what exactly is satellite connectivity? Before the world gets more of the new feature, let’s take a look at this emerging technology.
Look at the sky
The night sky is filled with satellites. Though you might not see any of them with the naked eye, they are all there in low Earth orbit (LEO). As you might imagine, their uses are aplenty. Most attribute LEO satellites to imaging, navigating, and measuring data. However, one emerging use is the improvement of connectivity for consumer devices.
Now, the biggest proponent of satellite internet is Starlink, a project of Elon Musk’s SpaceX. With over 300,000 satellites, the company’s satellite constellation provides internet to several countries including areas with low coverage. In fact, the company’s services are already somewhat in the Philippines.
Satellite internet does have its benefits. While the service isn’t the fastest, it offers connectivity that regular towers can’t normally reach. Imagine being out on a hike but you suddenly remember, oh my God, you left your stove running at home. Satellite internet will allow you to connect to the internet and notify a neighbor to check if your apartment has any wayward burn marks running up its walls.
Quite a feat, isn’t it? But is this what Apple just launched?
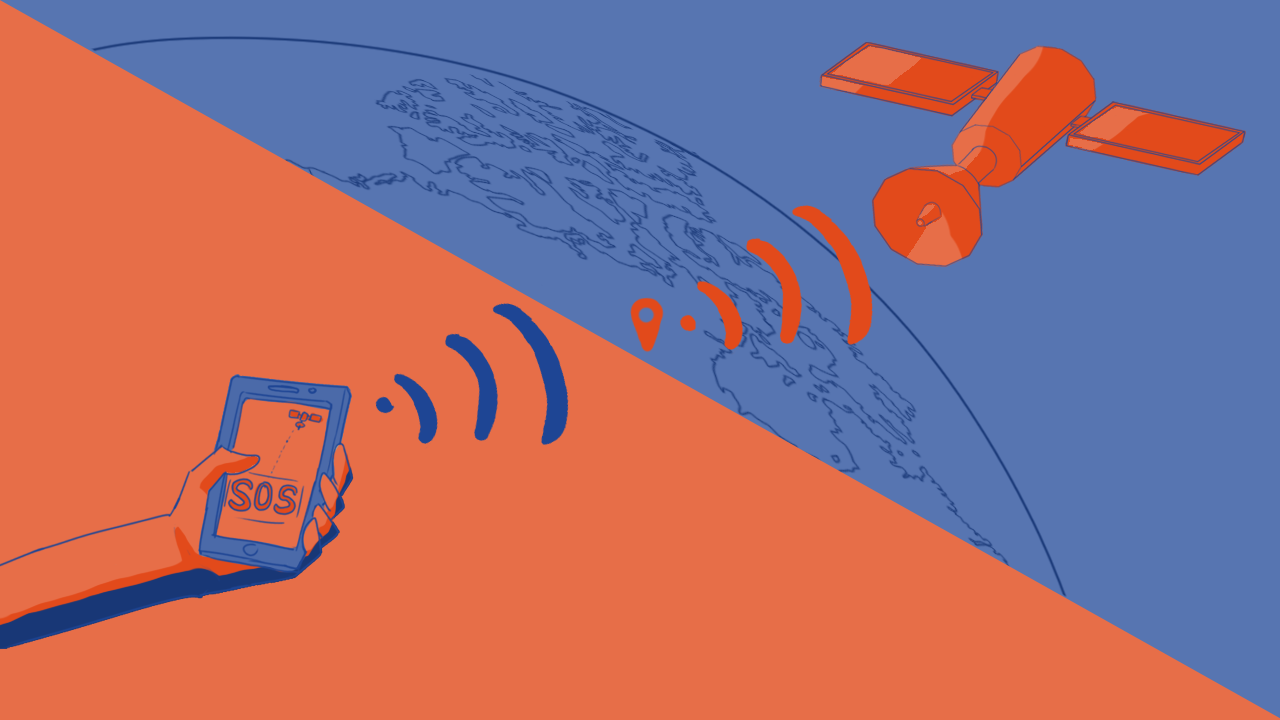
SOS, please someone help me
Contrary to what you might think, Apple’s new satellite connectivity doesn’t offer internet. It’s also not Starlink. Instead, it’s a simple SOS messaging service through the Globalstar satellite constellation. It won’t solve your faulty 5G service. However, it’ll help you in a pinch if you find yourself lost in the middle of nowhere.
Once again, imagine you’re out hiking. Suddenly, you fall down an unseen slope and break your ankle. You find yourself miles and miles away from civilization, and no one knows where you are. Apple’s satellite connectivity can help you send an SOS message to the authorities.
Here’s how it works. When you’re in a predicament, fire up the feature and point your phone towards the satellite nearest you. (Don’t worry; the phone will tell you where it is).
Now, it might take a few seconds to a minute before the phone can connect to a satellite — especially if the skies aren’t clear or if you’re underneath a canopy of trees. It might not even connect if the skies are completely obstructed. Regardless, while it tries to connect, the phone will ask a series of questions including who needs help and if anyone was harmed. This helps the phone craft and compress the necessary information for your message.
Because the service is only for emergencies, you can’t write an essay. Apple says that it will squeeze messages three time as small to ease transmission. It’s a wide-reaching 911 call for when you can’t actually call 911.
After compressing the message, the satellite will then beam the message to a nearby relay station on the ground, which will alert authorities for you.
Who can use it?
Naturally, only Apple users who have the latest devices will have the feature for now. Also, because it’s so new, it’s only coming to the United States and Canada with the upcoming iOS 16 update later this year. Of course, it might arrive to other territories soon after the initial launch.
China, however, is a no-go. Huawei launched its own satellite connectivity, packing the feature in the new Mate 50 series. If you’re in mainland China, you’ll have to use Huawei’s services.
Interestingly, Apple made it a point to say that the feature is free for the next two years. The implication seems clear: Users might have to fork over cash to keep the feature once the two years are up. Now, if you’re celebrating the coming of this arguably essential feature, the possibility of a paywall might leave a sour taste in your mouth. Should companies gatekeep who gets to send emergency messages in their time of need?
Passing fad or the future?
If you’re not a regular hiker, satellite connectivity might not appeal to you. However, it’s still interesting to wonder if the technology will make an impact outside of Apple. And it does seem that way.
It’s no coincidence that a few brands, including Apple and Huawei, have suddenly launched their own satellite connectivity features within a short span. Companies are putting a lot of money into the future of satellites. Very likely, Apple won’t be the last company to adopt the new feature.
Emergency satellite services are essential. Even if you don’t hike, you’ll never know when you might get into a precarious situation without cell coverage. Satellite connectivity mitigates that risk.
Now, how will the technology evolve beyond emergency services? Coupled with the efforts of Starlink, the early stages of satellite connectivity proves the concept of a satellite-laden future. Currently, a lot of services still struggle with the lack of towers in certain locations. The aid of satellites creates a future that won’t need towers everywhere. Though speed might be an issue, connectivity won’t.
That future is quite a possibility. However, it will also come with a host of questions. With space limited to only a handful of providers, will companies launch more satellites to address the potential need? How will space look like then? Will it just be a wasteland of used satellites? How much will everything cost? Though it’s coming, the future still has much to clarify.
Illustrations by Garel Perpetua.
-

 Reviews2 weeks ago
Reviews2 weeks agoThe Xiaomi Pad 6 is great for the editor on-the-go
-

 Reviews2 weeks ago
Reviews2 weeks agoHONOR 90 review: Simply bedazzling
-

 Gaming2 weeks ago
Gaming2 weeks agoRefurbished Steam Decks are now available through Valve
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoRedmi Watch 3 Active: Basic but better
-

 Gaming2 weeks ago
Gaming2 weeks agoRockstar officially partners with Grand Theft Auto V roleplay servers
-

 Gaming2 weeks ago
Gaming2 weeks agoPlayStation 5 Slim supposedly leaked online
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoCatch Cinemalaya 2023 films at Ayala Malls this weekend
-
 Apps2 weeks ago
Apps2 weeks agoSpotify DJ feature now available in the Philippines